Multiple stepper motors with joystick, TB6600 and the accelstepper library
In this video I show you how to control two independent stepper motors by a joystick using the accelstepper library and two TB6600 stepper motor controllers. The principle of the circuit is relatively simple, you just have to read the output voltage of each potentiometers in the joystick and determine a stepping speed based on those values. I really like this joystick, because it has a very good mechanism, and the potmeter is less noisy than the regular “PS2 joystick”.
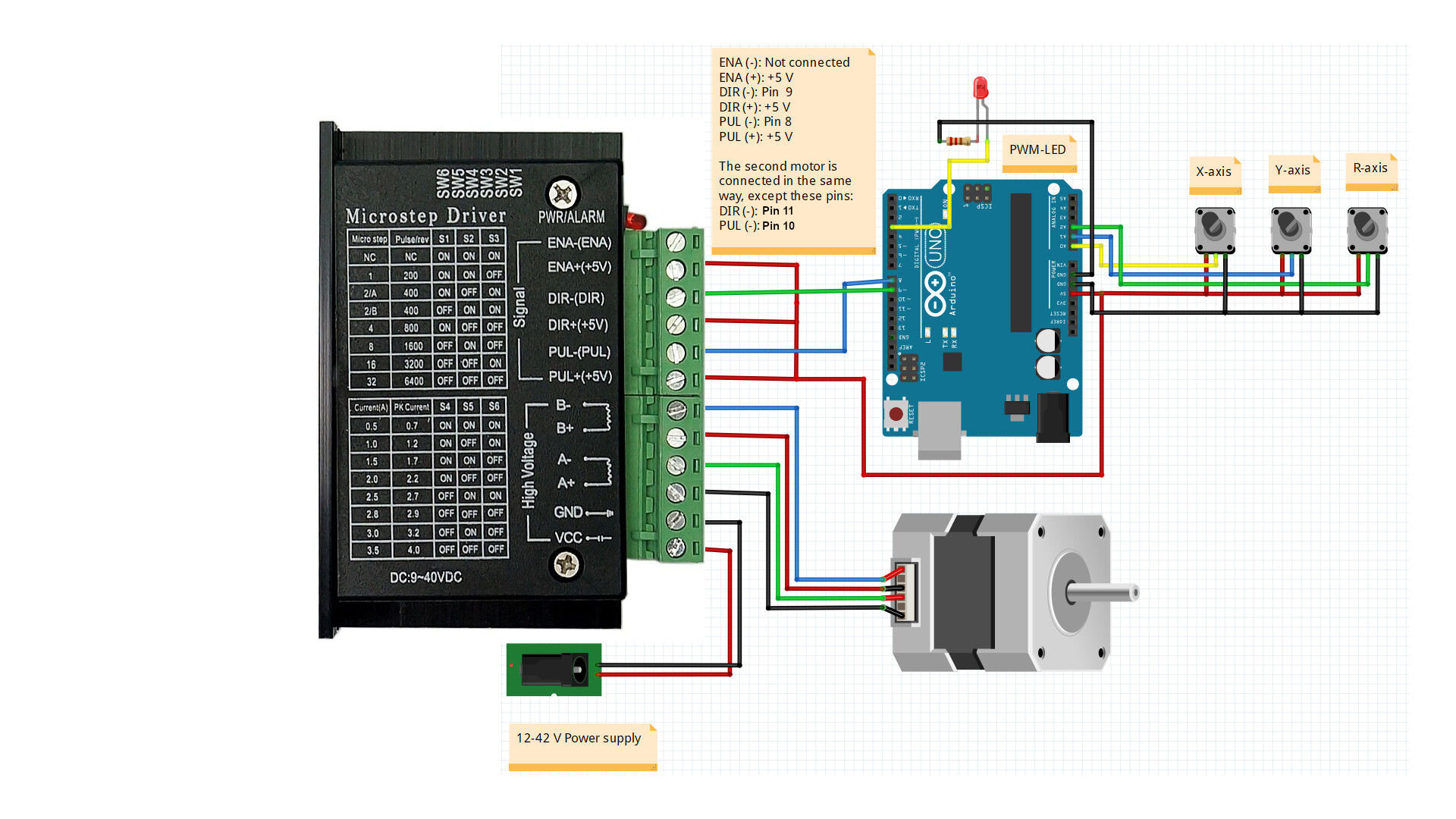
Wiring diagram
To avoid making the image too crowded, I just added 1 stepper motor and controller. The second motor is connected in the exact same way except its two signal pins which are connected to the Arduino. You can see it in the source code below too, but I connected the second TB6600 to the Pin 11 (DIR-) and Pin 10 (PUL-). The 3 potentiometers in the joystick is illustrated with the 3 potmeters. The LED is connected to Pin 3 which is the output of the PWM signal (see code below). The resistor’s value is 150 Ohm.
Arduino source code
#include <AccelStepper.h> //accelstepper library AccelStepper stepper(1, 8, 9); // direction Digital 9 (CCW), pulses Digital 8 (CLK) AccelStepper stepper2(1, 10, 11); // direction Digital 11 (CCW), pulses Digital 10 (CLK) //Pins const byte Analog_X_pin = A0; //x-axis readings const byte Analog_Y_pin = A1; //y-axis readings const byte Analog_R_pin = A2; //r-axis readings const byte LED_pin = 3; //PWM output for LED //Variables int Analog_X = 0; //x-axis value int Analog_Y = 0; //y-axis value int Analog_R = 0; //r-axis value int Analog_X_AVG = 0; //x-axis value average int Analog_Y_AVG = 0; //y-axis value average int Analog_R_AVG = 0; //r-axis value average int Analog_R_Value = 0; //this is used for the PWM value void setup() { //SERIAL Serial.begin(9600); //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //PINS pinMode(Analog_X_pin, INPUT); pinMode(Analog_Y_pin, INPUT); pinMode(Analog_R_pin, INPUT); pinMode(LED_pin, OUTPUT); //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- InitialValues(); //averaging the values of the 3 analog pins (values from potmeters) //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Stepper parameters //setting up some default values for maximum speed and maximum acceleration stepper.setMaxSpeed(5000); //SPEED = Steps / second stepper.setAcceleration(1000); //ACCELERATION = Steps /(second)^2 stepper.setSpeed(500); delay(500); //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- stepper2.setMaxSpeed(5000); //SPEED = Steps / second stepper2.setAcceleration(1000); //ACCELERATION = Steps /(second)^2 stepper2.setSpeed(500); delay(500); } void loop() { ReadAnalog(); stepper.runSpeed(); //step the motor (this will step the motor by 1 step at each loop indefinitely) stepper2.runSpeed(); } void ReadAnalog() { //Reading the 3 potentiometers in the joystick: x, y and r. Analog_X = analogRead(Analog_X_pin); Analog_Y = analogRead(Analog_Y_pin); Analog_R = analogRead(Analog_R_pin); //if the value is 25 "value away" from the average (midpoint), we allow the update of the speed //This is a sort of a filter for the inaccuracy of the reading if(abs(Analog_X-Analog_X_AVG)>25) { stepper.setSpeed(5*(Analog_X-Analog_X_AVG)); } else { stepper.setSpeed(0); } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- if(abs(Analog_Y-Analog_Y_AVG)>25) { stepper2.setSpeed(5*(Analog_Y-Analog_Y_AVG)); } else { stepper2.setSpeed(0); } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- if(abs(Analog_R-Analog_R_AVG)>25) { Analog_R_Value = map(Analog_R, 0, 1023, 0, 255); //10 bit ADC (0-1023) and 8 bit PWM (0-255) analogWrite(LED_pin, Analog_R_Value); //modify the PWM value } } void InitialValues() { //Set the values to zero before averaging float tempX = 0; float tempY = 0; float tempR = 0; //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //read the analog 50x, then calculate an average. //they will be the reference values for(int i = 0; i<50; i++) { tempX += analogRead(Analog_X_pin); delay(10); //allowing a little time between two readings tempY += analogRead(Analog_Y_pin); delay(10); tempR += analogRead(Analog_R_pin); delay(10); } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Analog_X_AVG = tempX/50; Analog_Y_AVG = tempY/50; Analog_R_AVG = tempR/50; //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Serial.print("AVG_X: "); Serial.println(Analog_X_AVG); Serial.print("AVG_Y: "); Serial.println(Analog_Y_AVG); Serial.print("AVG_R: "); Serial.println(Analog_R_AVG); Serial.println("Calibration finished"); }